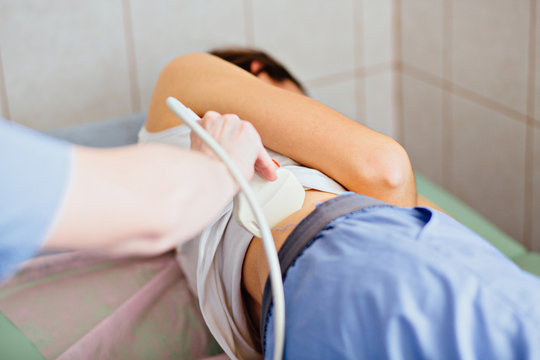
Renal ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic test that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the kidneys and surrounding organs. This test is an essential tool for diagnosing various kidney-related conditions and determining the underlying cause of symptoms such as abdominal pain, blood in the urine, or abnormal kidney function.
In this article, we will discuss what a renal ultrasound is, what to expect during the procedure, its benefits and limitations, and some common conditions that can be diagnosed with this test. So, let’s dive in and learn all you need to know about renal ultrasound.
Table of Contents
What is a Renal Ultrasound?
A renal ultrasound is a diagnostic imaging test that uses sound waves to produce images of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and surrounding organs. The test is performed by a trained healthcare professional, typically a sonographer or radiologist, using a small handheld device called a transducer.
During the test, the patient lies on their back while the transducer is placed on the skin above the kidney area. The transducer emits sound waves that bounce off the organs and tissues and create a picture on a computer screen. The images can help identify any abnormalities in the size, shape, or position of the kidneys, as well as detect any obstructions or blockages in the urinary system.
Why is a Renal Ultrasound Performed?
A renal ultrasound is performed for several reasons. The test is commonly used to evaluate kidney function and detect any abnormalities in the kidney structure, such as cysts or tumors. It can also identify any obstructions or blockages in the urinary system, such as kidney stones or tumors in the bladder.
The test is often used to diagnose conditions such as urinary tract infections, kidney stones, and kidney disease. It can also help monitor the progression of certain kidney-related conditions and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
A renal ultrasound is a safe and painless procedure that does not expose the patient to radiation. It is a useful diagnostic tool that can provide valuable information about the health of the kidneys and urinary system.
How to Prepare for a Renal Ultrasound
Preparing for a renal ultrasound is a straightforward process. In most cases, the patient will be asked to fast for several hours before the test to ensure that their bladder is empty. The patient may also be asked to drink a certain amount of water before the test to help fill the bladder, which can improve the quality of the images.
Patients should wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing and avoid wearing any jewelry or metal objects that may interfere with the test. They may also be asked to sign a consent form before the procedure.
It is essential to inform the healthcare provider of any medications the patient is taking, as some medications may need to be stopped before the test. Patients with pacemakers or other implanted medical devices should inform their healthcare provider before the test.
What to Expect During a Renal Ultrasound
A kidney ultrasound is a painless and non-invasive procedure that usually takes about 30 minutes to complete. The patient will be asked to lie on their back on an examination table, and a gel will be applied to the skin above the kidney area. The transducer is then placed on the skin and moved back and forth over the area.
The healthcare provider may ask the patient to change positions or hold their breath at certain times during the test to get a better view of the kidneys and surrounding organs. The patient may feel some pressure or discomfort as the transducer is pressed against the skin, but the procedure is generally well-tolerated.
After the test, the gel is wiped off the skin, and the patient can resume their normal activities. The images are reviewed by a radiologist or healthcare provider, who will discuss the results with the patient and recommend any further testing or treatment if necessary.
Benefits and Limitations of Ultrasound
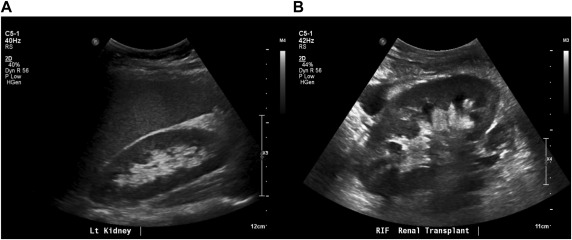
There are several benefits to using a renal ultrasound as a diagnostic tool. It is a non-invasive procedure that does not expose the patient to ionizing radiation. It is also a relatively quick and painless procedure that can provide valuable information about the health of the kidneys and surrounding organs.
However, there are some limitations to the test. The images produced by a kidney ultrasound may not be as detailed as those obtained from other imaging tests, such as a CT scan or MRI. In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to confirm a diagnosis or provide more detailed information about a particular condition.
Additionally, a kidney ultrasound may not be effective in detecting certain types of kidney stones or tumors, which may require other imaging tests or procedures for diagnosis.
Common Conditions Diagnosed with Renal Ultrasound
Renal ultrasound is a useful tool for diagnosing a wide range of kidney-related conditions. Some of the most common conditions that can be diagnosed with a ultrasound include:
Kidney stones: A ultrasound can detect the presence of kidney stones and evaluate their size and location.
Urinary tract infections: A ultrasound can identify any blockages or abnormalities in the urinary system that may be causing a urinary tract infection.
Kidney cysts: A ultrasound can detect the presence of cysts in the kidneys, which may be indicative of a kidney disease.
Tumors: A ultrasound can detect the presence of tumors in the kidneys or surrounding organs.
Hydronephrosis: A ultrasound can detect the presence of hydronephrosis, which is a condition in which the kidney becomes swollen due to a buildup of urine.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a renal ultrasound is a vital diagnostic tool for evaluating kidney function and detecting abnormalities in the urinary system. The test is safe, non-invasive, and relatively quick and painless. It is commonly used to diagnose a wide range of kidney-related conditions, including kidney stones, urinary tract infections, and kidney cysts. Learn What is a Pelvic Ultrasound? Everything You Need to Know